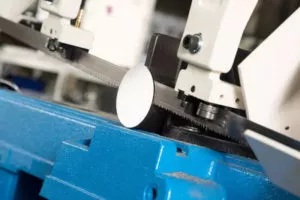
In this article, we dive into the technical nuances of pull-down operations versus gravity feed operations in metal cutting bandsaws. You’ll learn how each system works, the advantages and challenges they present, and why one might be preferable depending on your cutting needs. We’ll also cover essential setup requirements, maintenance tips, and emerging trends to keep you ahead in the metal cutting game.
Exploring Metal Cutting Bandsaws Feed Mechanisms
Metal cutting bandsaws are essential tools in various manufacturing and fabrication processes, and their efficiency largely depends on the type of feed mechanism employed. Feed mechanisms are the systems that control how the material is moved through the cutting zone, directly influencing the quality of the cut and the overall productivity of the operation. Understanding these mechanisms is crucial for operators and manufacturers alike, as they can significantly affect cutting speed, precision, and material waste.
In the context of metal cutting bandsaws, feed mechanisms can be defined as the methods by which the saw blade engages with the material being cut. This involves the application of force to push the material into the blade, which can be achieved through various means. Key terminologies associated with feed mechanisms include:
- Feed Rate: The speed at which the material is fed into the blade, typically measured in inches per minute.
- Kerf: The width of the cut made by the blade, which can impact material waste.
- Downforce: The force applied to the blade to ensure effective cutting, which can be adjusted based on material type.
These mechanisms work by either utilizing gravity, hydraulic systems, or manual operation to move the material through the cutting zone. The choice of feed mechanism can greatly influence the efficiency and effectiveness of the cutting process.
Defining Feed Mechanisms in Metal Cutting Bandsaws
Feed mechanisms in metal cutting bandsaws are critical for ensuring that the material is cut accurately and efficiently. They determine how the material is positioned and moved into the blade, which is essential for achieving precise cuts. The mechanisms can be broadly categorized into two types: gravity feed and pull-down operations. Each type has its own unique characteristics and operational principles that affect the cutting process.
Overview of Common Feed Operations – Gravity Feed and Pull-Down
Gravity feed and pull-down operations are the two primary feed mechanisms used in metal cutting bandsaws. Here’s a detailed comparison of how each method functions:
- Gravity Feed:
- Relies on the weight of the saw head to apply downward pressure on the material.
- Typically slower and more controlled, making it suitable for delicate cuts.
- Commonly used in smaller or manual bandsaws.
- Pull-Down:
- Utilizes a powered mechanism to pull the blade down through the material.
- Allows for faster cutting speeds and is often used in industrial applications.
- Can reduce operator fatigue and improve efficiency in high-volume cutting tasks.
How Feed Mechanism Influences Cutting Precision
The choice of feed mechanism has a significant impact on cutting precision. Gravity feed systems tend to provide a more controlled cutting environment, which can lead to better kerf quality and reduced material waste. In contrast, pull-down systems, while faster, may require careful calibration to avoid excessive force that could lead to blade wear or material deformation.
Technical data suggests that gravity feed systems can achieve kerf widths as narrow as 0.025 inches, while pull-down systems may produce wider kerfs due to the increased cutting speed. Expert opinions emphasize the importance of selecting the appropriate feed mechanism based on the material being cut and the desired precision level. For instance, softer materials may benefit from the gentler approach of gravity feed, while harder materials may require the aggressive cutting action of pull-down systems.
Technical Requirements and Setup Considerations
Setting up different feed mechanisms in metal cutting bandsaws involves specific technical requirements and considerations. For gravity feed systems, operators must ensure that the weight distribution is balanced and that the feed rate is adjustable to accommodate various material types. Calibration processes often involve testing different weights and settings to find the optimal configuration for the material being cut.
In contrast, pull-down systems require careful attention to hydraulic pressure settings and blade tension. Operators should regularly check the hydraulic fluid levels and ensure that the system is calibrated for the specific cutting task. Practical tips for optimal performance include maintaining a clean cutting area, regularly inspecting the blade for wear, and adjusting the feed rate based on the material’s hardness and thickness.
Switching between pull-down and gravity feed is like choosing a superhero’s power—one gives you lightning-fast cuts while the other saves the day with precision, all while keeping the metal crumbs in check!
Deep Dive into Gravity Feed Operations in Metal Cutting Bandsaws
Principles and Mechanics of Gravity Feed
Gravity feed operations in metal cutting bandsaws rely on the natural force of gravity to drive the cutting process. In this system, the saw blade is mounted on a pivoting arm that is raised and then allowed to descend under its own weight. The mechanics of this operation can be broken down into several key components:
- Pivot Arm: The saw blade is attached to a pivot arm that can be raised and lowered. The angle of the arm can often be adjusted to accommodate different cutting angles.
- Weight Adjustment: Many gravity feed bandsaws feature adjustable weights or counterbalances that can be modified to control the descent speed of the blade, allowing for precise cutting pressure.
- Cutting Force: The cutting force is determined by the weight of the saw arm and any additional weights applied. This force can be fine-tuned to suit the material being cut, ensuring optimal performance.
- Blade Speed Control: While gravity provides the downward force, the speed of descent can be regulated using dampers or hydraulic systems to prevent excessive feed rates, especially on softer materials.
Advantages: Energy Efficiency and Simplicity
Gravity feed bandsaws offer several advantages that make them a popular choice in various metalworking applications:
- Energy Efficiency: Since gravity is the primary force driving the cutting process, these systems consume less energy compared to hydraulic or electric feed systems.
- Simplicity of Design: The mechanical simplicity of gravity feed systems often results in lower maintenance requirements and reduced operational complexity.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Gravity feed bandsaws are typically less expensive to manufacture and purchase, making them accessible for small workshops and fabricators.
- Operator Control: Operators can easily adjust the cutting pressure by modifying the weight settings, allowing for greater control over the cutting process.
- Reduced Operator Fatigue: The reliance on gravity minimizes the physical effort required from operators, making it easier to manage longer cutting sessions.
Common Applications and Material Considerations
Gravity feed operations are particularly effective in specific scenarios and industries:
- Metal Fabrication: Commonly used in metal fabrication shops for cutting various metals, including aluminum, steel, and brass.
- Small Batch Production: Ideal for small to medium-sized production runs where precision and control are paramount.
- Custom Cuts: Frequently employed for custom cuts and intricate designs, as the operator can easily adjust the feed rate and pressure.
- Material Thickness: Best suited for materials of moderate thickness, as very thick or hard materials may require more force than gravity can provide effectively.
Challenges and Troubleshooting Tips for Gravity Feed Systems
While gravity feed systems are advantageous, they also come with challenges that operators should be aware of:
- Inconsistent Cutting Pressure: If the weight settings are not properly adjusted, it can lead to inconsistent cutting pressure, resulting in poor cut quality. Regularly check and calibrate the weights.
- Blade Dulling: Excessive feed rates can dull the blade quickly. Operators should monitor the cutting speed and adjust the weight accordingly to maintain optimal performance.
- Material Slippage: If the material is not secured properly, it may slip during cutting. Ensure that the workpiece is clamped securely before starting the cut.
- Hydraulic Dampers Maintenance: If the system uses hydraulic dampers for speed control, regular maintenance is essential to prevent leaks and ensure smooth operation.
In-Depth Look at Pull-Down Operations in Metal Cutting Bandsaws
Understanding the Pull-Down Mechanism and Its Operation
The pull-down operation in metal cutting bandsaws is a sophisticated mechanism designed to enhance cutting efficiency and precision. This system operates by utilizing a weighted arm that descends onto the workpiece, applying consistent pressure throughout the cutting process. The mechanism is engineered to ensure that the blade maintains optimal contact with the material, which is crucial for achieving clean cuts and minimizing blade wear.
In a typical pull-down bandsaw, the operator initiates the cut by activating the saw, which then allows the blade to descend under the influence of gravity or a hydraulic system. This controlled descent is often adjustable, enabling operators to set the feed rate according to the material being cut. The design of the pull-down mechanism often incorporates features such as dampers or counterweights to regulate the speed of descent, preventing excessive force that could damage the blade or the workpiece.
Technical insights reveal that the pull-down mechanism can be integrated with advanced features such as programmable feed rates and automatic shut-off systems, which enhance operational safety and efficiency. This level of engineering not only improves the quality of the cut but also extends the lifespan of the bandsaw blade, making it a preferred choice in high-volume manufacturing environments.
Comparative Advantages: Speed and Operator Interaction
Pull-down systems offer several advantages over traditional gravity feed mechanisms, particularly in terms of operational speed and the level of operator interaction required. Here are some key benefits:
- Increased Cutting Speed: Pull-down bandsaws can achieve faster cutting rates due to their ability to apply consistent pressure, which reduces the time taken to complete cuts.
- Reduced Operator Fatigue: The automated nature of pull-down systems minimizes the physical effort required from operators, allowing for longer periods of operation without fatigue.
- Enhanced Precision: The controlled descent of the blade ensures that cuts are more accurate, reducing the likelihood of errors that can occur with manual feed systems.
- Versatility: Pull-down bandsaws can be easily adjusted for different materials and thicknesses, making them suitable for a wide range of applications.
For example, in a manufacturing setting where aluminum and steel are frequently cut, a pull-down bandsaw can be quickly recalibrated to accommodate the different densities and cutting requirements of these materials, thus optimizing production efficiency.
Technical Specifications and Setup Requirements
Setting up a pull-down bandsaw requires careful attention to technical specifications to ensure optimal performance. Key parameters include:
- Blade Size: The blade must be compatible with the machine’s specifications, typically ranging from 1/2 inch to 1 inch in width.
- Motor Power: A robust motor, often rated between 1 to 3 horsepower, is essential for maintaining cutting speed and efficiency.
- Feed Rate Adjustment: The ability to adjust the feed rate is crucial for different materials; this can be achieved through mechanical or electronic controls.
- Safety Features: Incorporating safety mechanisms such as blade guards and emergency shut-off switches is vital for operator safety.
Installation procedures typically involve calibrating the blade tension, aligning the blade guides, and ensuring that the hydraulic or pneumatic systems are functioning correctly. Regular maintenance checks should also be scheduled to monitor the condition of the blade and the overall machine performance.
Best Practices for Maintaining Pull-Down Systems
Maintaining pull-down bandsaws is essential for ensuring longevity and optimal performance. Here are some best practices:
- Regular Blade Inspection: Check for wear and damage regularly, replacing blades as necessary to maintain cutting quality.
- Lubrication: Ensure that all moving parts are adequately lubricated to reduce friction and wear.
- Calibration: Periodically recalibrate the machine settings to ensure that the blade tension and feed rates are optimal for the materials being cut.
- Cleaning: Keep the machine clean from debris and chips to prevent operational issues and maintain a safe working environment.
Real-world case studies have shown that companies implementing these maintenance practices have significantly reduced downtime and improved overall productivity. For instance, a manufacturing facility that adopted a rigorous maintenance schedule for its pull-down bandsaws reported a 30% increase in cutting efficiency and a notable decrease in blade replacement costs.
Comparative Analysis: Pull-Down vs. Gravity Feed in Metal Cutting Bandsaws
Performance Metrics and Productivity Impact
When comparing pull-down and gravity feed operations in metal cutting bandsaws, performance metrics such as cutting speed, efficiency, and overall productivity are critical. Pull-down bandsaws typically offer faster cutting speeds due to their active feed mechanism, which allows for greater control over the cutting process. According to industry data, pull-down systems can achieve cutting rates of up to 50% faster than gravity feed systems, particularly in high-volume production environments.
Gravity feed systems, while generally slower, excel in applications requiring precision and minimal operator intervention. The weight of the saw head provides a consistent downward force, which can be beneficial for cutting softer materials. However, this can lead to longer cycle times, especially when cutting thicker or harder materials. Experts suggest that for operations focused on high throughput, pull-down systems are often the preferred choice, while gravity feed systems may be more suitable for specialized tasks where precision is paramount.
Quality of Cut: Precision, Kerf, and Material Waste
The quality of cut produced by both mechanisms varies significantly, impacting kerf width and material waste. Key factors include:
- Precision: Pull-down bandsaws generally provide a more consistent cut due to their controlled feed rate, which minimizes blade deflection.
- Kerf Width: Gravity feed systems may produce a wider kerf due to the less controlled descent of the blade, leading to increased material waste.
- Material Waste: Pull-down systems tend to generate less waste, as they can be adjusted for optimal cutting pressure, reducing the likelihood of blade binding or excessive wear.
In applications where material conservation is critical, the pull-down mechanism often proves advantageous, while gravity feed systems may be more appropriate for less critical cuts.
Safety, Reliability, and Operator Fatigue
Safety is a paramount concern in any machining operation. Pull-down bandsaws often incorporate advanced safety features, such as automatic shut-off mechanisms and improved blade guards, which can reduce the risk of accidents. In contrast, gravity feed systems, while generally safe, may require more manual intervention, increasing the potential for operator fatigue and error.
Reliability also varies between the two systems. Pull-down bandsaws are typically more robust, designed for continuous operation in demanding environments. Conversely, gravity feed systems may experience wear and tear more quickly due to their reliance on gravity for feed pressure, which can lead to inconsistent performance over time. Industry experts recommend regular maintenance and operator training to mitigate these risks and enhance safety across both systems.
Use-Case Scenarios and Cost Analysis
Choosing between pull-down and gravity feed systems often depends on specific use-case scenarios:
- Pull-Down Systems: Ideal for high-volume production environments where speed and efficiency are critical. Commonly used in manufacturing settings where rapid cuts are necessary.
- Gravity Feed Systems: Best suited for applications requiring precision and minimal operator fatigue, such as custom fabrication or intricate cuts.
Cost analysis reveals that while pull-down systems may have a higher initial investment, their efficiency can lead to lower operational costs over time. Gravity feed systems, being generally less expensive, may appeal to smaller shops or those with limited budgets, but could incur higher material costs due to increased waste.
Optimizing Feed Operation Settings for Enhanced Machining Productivity
Feed Pressure Adjustment and Control Techniques
Optimizing feed pressure is crucial for achieving the best cutting performance in metal cutting bandsaws. Here are several techniques to adjust feed pressure effectively:
- Adjustable Weights: Utilize movable counterweights to fine-tune the feed pressure. For instance, in gravity feed systems, adjusting the weight can help control the descent speed of the saw blade.
- Spring Counterbalance: Implement a screw-thread coil spring to adjust the feed pressure dynamically. This method allows for quick adjustments based on the material being cut.
- Hydraulic Feed Control: Use hydraulic systems to maintain consistent pressure. For example, hydraulic feed saws can adjust the cutting force based on the material’s resistance, ensuring optimal performance.
- Pneumatic Dampers: Incorporate pneumatic dampers to control the speed of descent in gravity feed saws. This prevents excessive feed pressure on softer materials, reducing the risk of blade damage.
Maintenance Protocols for Consistent Performance
Regular maintenance is essential for ensuring consistent feed operation performance. Here are key protocols to follow:
- Daily Checks: Inspect the blade tension and alignment before each shift. Ensure that the blade is properly tensioned to avoid vibrations that can affect cut quality.
- Lubrication: Regularly lubricate moving parts, including the feed mechanism and guide rollers, to minimize wear and tear.
- Blade Cleaning: Use a chip brush to remove debris from the blade after each use. This helps maintain cutting efficiency and prolongs blade life.
- Calibration: Periodically calibrate the feed rate settings according to the material type and thickness. This ensures that the machine operates within optimal parameters.
- Troubleshooting: If performance issues arise, refer to a troubleshooting guide to identify and rectify common problems, such as misalignment or excessive wear.
Troubleshooting Common Feed Mechanism Problems
Feed mechanisms can encounter various issues that affect performance. Here are common problems and expert tips for troubleshooting:
- Inconsistent Feed Rate: Check for debris in the feed mechanism. Clean any obstructions and ensure that the feed rollers are functioning smoothly.
- Blade Binding: If the blade binds during operation, inspect the alignment of the blade guides. Adjust them to ensure they are not too tight against the blade.
- Excessive Vibration: Vibration can indicate improper blade tension or a dull blade. Ensure the blade is sharp and properly tensioned to reduce vibrations.
- Uneven Cuts: If cuts are uneven, verify that the material is securely clamped and that the feed rate is appropriate for the material type.
- Hydraulic Issues: For hydraulic systems, check fluid levels and inspect for leaks. Low fluid levels can lead to inconsistent feed pressure.
Implementing Best Practice Guidelines from Industry Insights
To enhance machining productivity, consider these best practice guidelines derived from industry research:
- Material-Specific Settings: Adjust feed rates based on the material being cut. For example, softer materials may require a higher feed rate, while harder materials need a slower approach.
- Regular Training: Ensure operators are trained on the specific feed mechanisms of the bandsaw. Knowledge of machine capabilities can significantly improve productivity.
- Data Monitoring: Implement monitoring systems to track feed performance and blade wear. This data can help in making informed adjustments to settings.
- Utilize Advanced Technology: Consider integrating CNC controls for automated feed adjustments based on real-time cutting conditions.
- Feedback Loops: Establish a feedback system where operators can report issues or suggest improvements based on their experiences with the feed mechanisms.
Future Trends and Advanced Techniques in Bandsaw Feed Mechanisms
Innovations in Hydraulic and Automated Feed Systems
The landscape of bandsaw feed mechanisms is rapidly evolving, driven by advancements in hydraulic and automated systems. These innovations are enhancing precision, efficiency, and user experience in metal cutting operations. Recent developments include:
- Smart Hydraulic Systems: New hydraulic systems are being designed with integrated sensors that monitor pressure and flow rates in real-time, allowing for precise adjustments during cutting operations.
- Automated Feed Control: Advanced automated systems now utilize programmable logic controllers (PLCs) to optimize feed rates based on material type and thickness, significantly reducing operator intervention.
- Energy Efficiency: Innovations in hydraulic pump design are leading to reduced energy consumption, making bandsaws more environmentally friendly and cost-effective to operate.
- Adaptive Feed Mechanisms: New adaptive technologies allow bandsaws to automatically adjust feed rates based on the resistance encountered during cutting, improving blade life and cut quality.
The Role of CNC Controls and Sensor-Driven Adjustments
CNC controls and sensor-driven adjustments are revolutionizing the way bandsaws operate. These technologies provide unprecedented levels of precision and automation. For instance:
Modern CNC bandsaws can be programmed to execute complex cutting patterns with minimal human oversight. This capability is particularly beneficial in high-volume production environments where consistency is key.
Additionally, sensors can detect variations in material density and automatically adjust the feed rate to maintain optimal cutting conditions. According to industry experts, this not only enhances the quality of the cut but also extends the lifespan of the blade by reducing wear.
For example, a study by the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) highlighted that CNC-controlled bandsaws could achieve a 30% increase in cutting efficiency compared to traditional manual systems.
Integration with Next-Generation Metalworking Technologies
Emerging metalworking technologies are increasingly being integrated with advanced bandsaw feed mechanisms. This integration is paving the way for smarter manufacturing processes. Notable examples include:
- IoT Connectivity: Bandsaws equipped with Internet of Things (IoT) capabilities can communicate with other machines and systems, allowing for real-time data sharing and process optimization.
- Machine Learning Algorithms: Some manufacturers are implementing machine learning algorithms that analyze cutting data to predict maintenance needs and optimize feed settings automatically.
- Case Studies: Leading manufacturers like XYZ Corp have reported a 25% reduction in material waste and a 15% increase in productivity after integrating IoT-enabled bandsaws into their production lines.
Forecasting Operational Efficiency Improvements
Looking ahead, the adoption of advanced feed mechanisms is expected to significantly enhance operational efficiency in bandsaw operations. Predictions indicate:
- Cost Savings: Companies could see a reduction in operational costs by up to 20% due to decreased material waste and improved energy efficiency.
- Increased Throughput: Enhanced automation and precision are likely to lead to a 30% increase in throughput, allowing manufacturers to meet growing demand without compromising quality.
- Expert Insights: Industry analysts predict that by 2025, 70% of metal cutting operations will utilize automated feed systems, underscoring the shift towards more efficient manufacturing practices.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are pull-down operations in metal cutting bandsaws?
Pull-down operations involve a powered mechanism that actively pulls the blade downward, allowing for faster cutting speeds and improved efficiency in high-volume production environments.
What is the key principle behind gravity feed operations in metal cutting bandsaws?
Gravity feed operations rely on the weight of the saw head to naturally force the blade into the material, offering a controlled cut ideal for precision work.
What are the benefits of using pull-down systems over gravity feed in metal cutting?
Pull-down systems provide increased cutting speeds, reduce operator fatigue, and offer enhanced precision through controlled feed rates, making them suitable for high-volume and demanding cuts.
How do gravity feed systems maintain cutting precision?
Gravity feed systems use the consistent downward force created by the saw head’s weight, which can be fine-tuned with adjustable counterweights, ensuring a steady, controlled cut that minimizes material waste.
What technical requirements should be considered for pull-down systems?
Key considerations include ensuring the correct blade size, maintaining optimal motor power, carefully adjusting feed rate settings, and integrating safety features like blade guards and emergency shut-offs.
How do hydraulic systems enhance pull-down operations?
Hydraulic systems in pull-down operations control blade descent with precision, allowing adjustments in feed pressure and speed which leads to improved cutting quality and longer blade life.
What maintenance protocols are recommended for gravity feed bandsaws?
Routine maintenance for gravity feed systems includes regular calibration of weight settings, checking blade tension and alignment, cleaning debris from the blade, and ensuring hydraulic dampers are leak-free and properly adjusted.
How does material thickness influence the choice between pull-down and gravity feed operations?
Thicker or harder materials often require the aggressive cutting action of pull-down systems, while thinner or more delicate materials might benefit from the controlled descent of gravity feed systems.
What impact do feed mechanisms have on kerf quality and material waste?
Pull-down mechanisms can minimize material waste by providing a more consistent cut with a narrower kerf, whereas gravity feed systems may produce wider kerfs if the descent is not finely controlled.
What future trends are emerging in bandsaw feed mechanisms?
Emerging trends include the integration of smart hydraulic systems, sensor-driven adjustments, CNC controls, and IoT connectivity, all designed to improve efficiency, precision, and overall operational efficiency in metal cutting bandsaws.